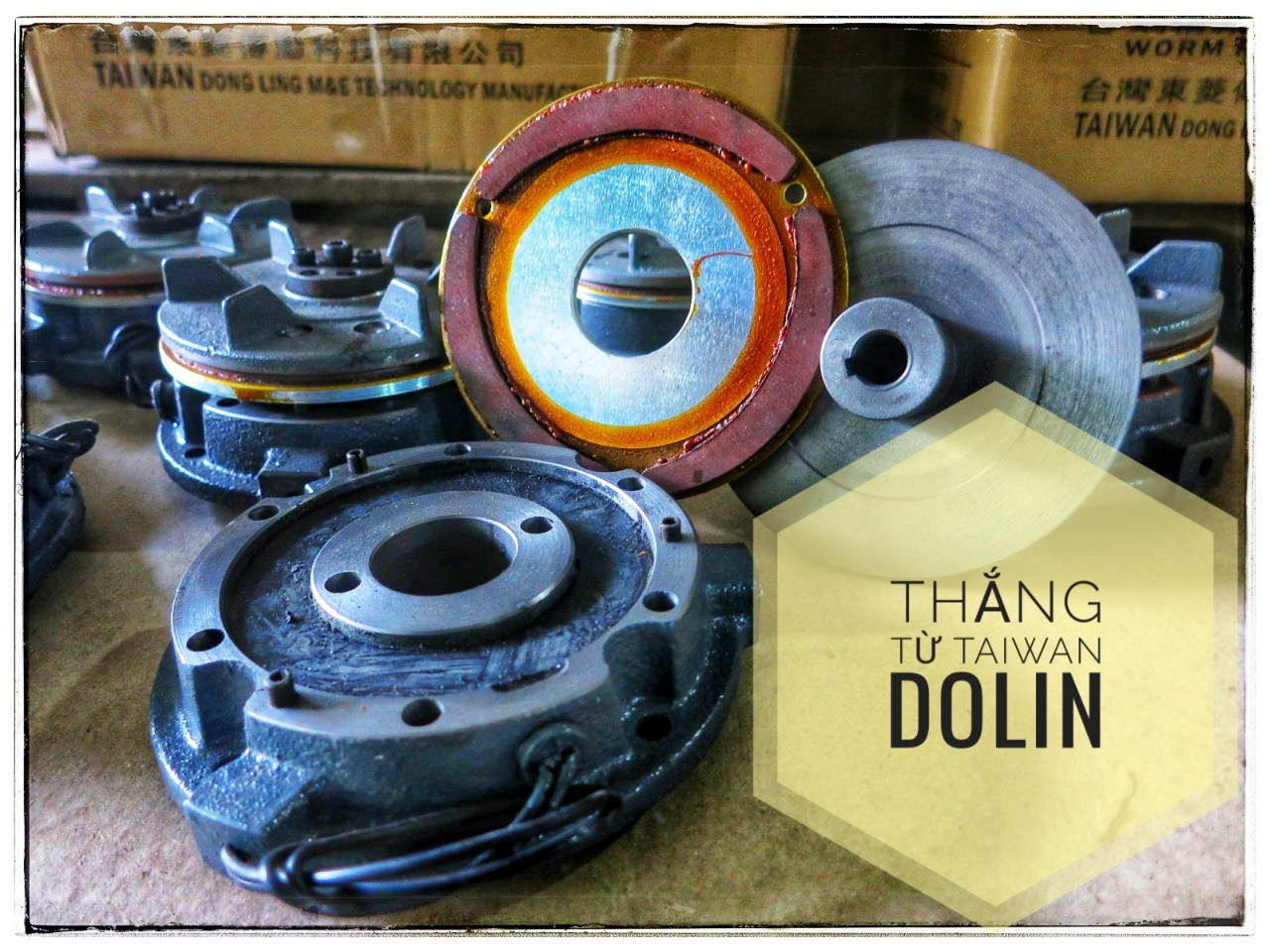
The motor brake is a braking system integrated directly into the engine. It is powered by electricity and generates resistance or braking force to control the movement of the motor or device to which it is applied. The working principle of electromagnetic brake is to generate friction or electromagnetic force to slow down, stop or keep the motor in a specific position.
Brakes are used in industrial production and transportation. In fact, there are two common situations during operation when a magnetic brake must be used to stop the motor:
- When a problem occurs or a sudden stop of the machine is required.
- Eliminates the moment of inertia when the engine is turned off.
Brakes or magnetic brakes are another name for brakes.
Structure of motor brake (motor)
The basic structure of the motor brake (also called the magnetic brake on the motor) consists of the following parts:
- Magnet Set: This is the component that generates the magnetic force to win. Magnetic units usually consist of a conductive coil and a magnetic core that can create an attractive or repulsive force when current passes through it.
- Resistance Group: The resistance group is used to generate friction or braking force. It can be a metal part, such as a brake plate, or a magnetic part, such as a magnetic fork. When the drag unit comes into contact with the magnetic unit, a force is generated that prevents the motor from moving.
- Control system: The braking of the motor is controlled by the electrical control system. The system includes devices such as controllers, switches, and circuits that activate and control the operation of the magnetic brake.
- Cooling system: Due to the friction caused by motor braking, the temperature will increase, so a cooling system is used to reduce the temperature and ensure the stable operation of the magnetic brake.
- Mechanical mechanism: Motor brakes usually have a mechanical mechanism, such as an actuator or gearbox, to transmit the force of the magnetic brake to the motor or other device.
The construction of brakes used on electric motors can vary depending on the specific type and application. Some complex models may include additional components such as damping systems, dual actuators, or other adjustment mechanisms to enhance performance and controllability.
The advantages and disadvantages of winning words
advantage
Motion Control: Magnetic brakes precisely control the movement of motors or equipment. It can stop or decelerate flexibly and precisely, ensuring safety and performance during operation.
Direct integration: The motor’s brake is integrated directly into the engine, reducing space and simplifying the braking system. This creates a space-saving solution and is easy to deploy in applications with high size requirements.
Convenient control: The braking of the motor can be electronically controlled, which means it can be controlled accurately and flexibly by remote or automatic control systems. This simplifies the operation process and increases safety.
shortcoming
Temperature: Using the motor brake for a long time or with high power will generate high temperatures. This affects the performance and life of the braking system and engine.
Power limitation: The motor holding brake has power limitation and is not suitable for applications with higher power requirements. In these cases, other braking systems, such as hydraulic brakes, can be used instead.
Practical applications of motor braking
Industry and Machinery: Magnetic brakes are widely used in industry to control motor movement and ensure safety during operation. Applications include industrial machinery, manufacturing machines, industrial robots and automation systems.
Cars and Trams: In cars and electric vehicles, electromagnetic brakes are used to control speed and stop the vehicle smoothly and safely. It provides energy regeneration during braking, improving system performance and durability.
Elevator Systems: Motor brakes are also used in elevator systems to maintain position or prevent movement when power is lost. This ensures safety and prevents falls during a power outage.
The above is information about motor brakes, including their advantages and disadvantages and their applications. The use of electromagnetic brakes depends on the specific requirements of each application and other technical factors.