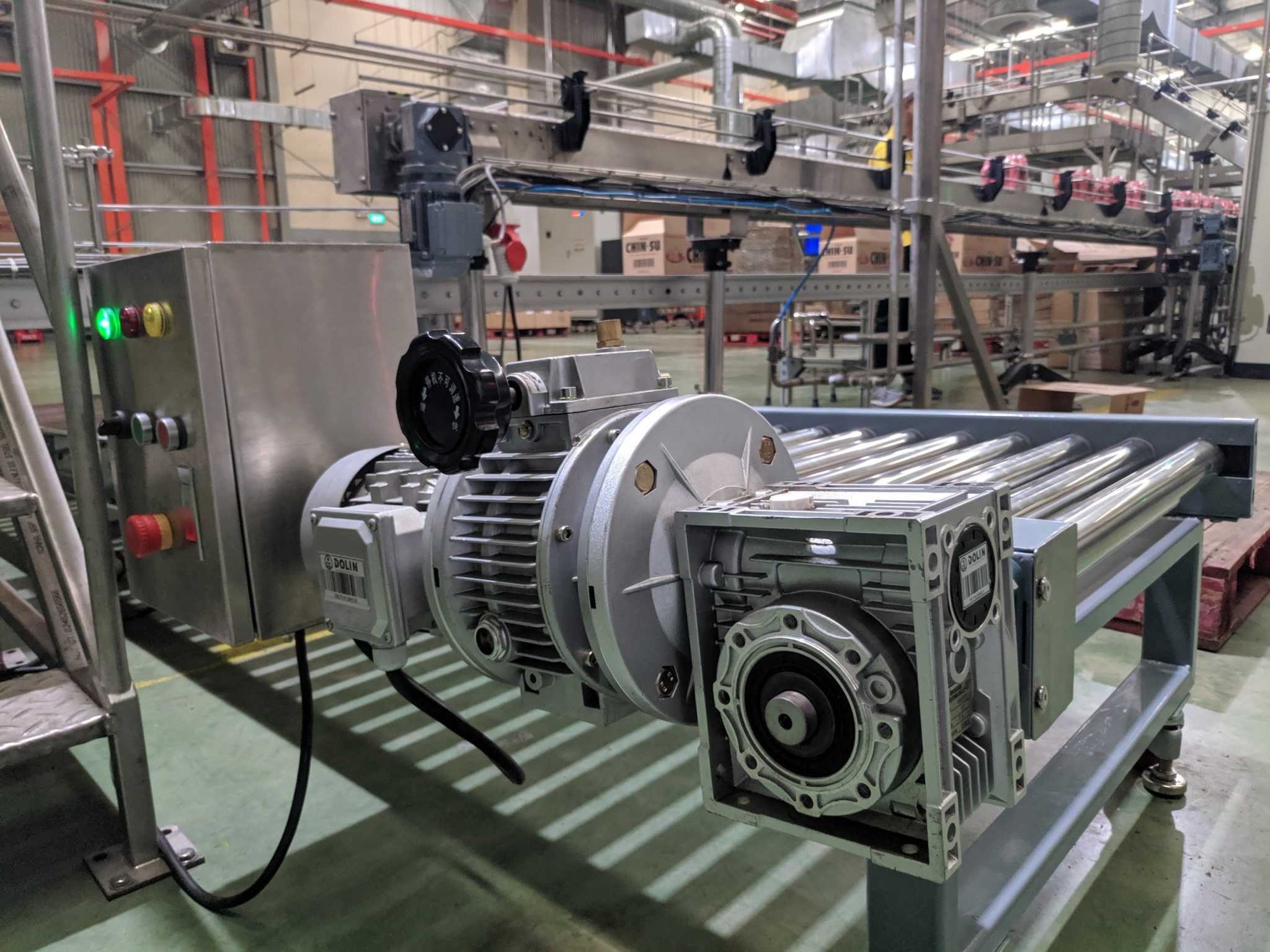
Overview of continuously variable speed motors
Continuously variable speed motors are commonly used in industrial production and automation applications. Continuously variable speed motors have the ability to adjust speed, improving efficiency and saving energy during the production process.
Types of Today’s Continuously Variable Speed Motors
There are two main types of continuously variable speed motors:
Synchronous motors and asynchronous motors. Synchronous motors are used when synchronization of motor speed and mains frequency is required. Asynchronous motors are used where synchronization is not required and the speed can be adjusted by the mains frequency or a frequency converter.
- Synchronous Motor: A synchronous motor is a motor with a fixed synchronous speed based on the mains frequency. The higher the speed of this motor, the power supply frequency must also be increased accordingly. For synchronous motors, speed regulation via the mains frequency is not the best solution.
- Asynchronous motor: An asynchronous motor is a motor whose rotation speed is not synchronized with the power frequency. For this motor, the motor speed does not depend on the mains frequency but on the input voltage. Asynchronous motors can have their speed controlled by the frequency of the power supply or by a frequency converter.
Applications of continuously variable speed motors
Continuously variable speed motors are widely used in industrial production such as food and beverage production, papermaking, textiles, woodworking, and shipbuilding. It is also used in hydraulic and mechanical applications and automatic control systems.
Advantages of using continuously variable speed motors
There are many benefits to using continuously variable speed motors, including:
- Improve the operating efficiency of production systems
- Save energy and reduce operating costs
- Ensure accuracy and synchronization of production processes
- Minimize noise and vibration levels during operation
- Ensure the safety of users and production equipment